

- LINUX GRSYNC UPDATE
- LINUX GRSYNC DOWNLOAD
My personal default set of parameters for rsync end up being -avuP (archive, verbose output, update only new files, and show the progress of the work being done). -include-from=FILE : Same as above, but read from a file.-include=PATTERN : Also used to negate the exclusion rules.-exclude-from=FILE : Same as above, but read from a file.-exclude=PATTERN : Use PATTERN to exclude files from the sync.-files-from=FILE : Read list source files from a text file.-existing : Only update files, but don’t create new ones that are missing.-c : Use a checksum value to determine which files to skip, rather than the modification time and size.Useful for inclusion in scripting when the terminal output is not required -u : Skip updating target files if they are newer than the source.-v : Show progress overall, outputting information about each file as it completes it.
 -list-only : Only show the list of files that rsync would transfer. -n : Dry run the command without transferring files. But, some of those might be contrary to what a user needs, so breaking it out into the specific functionality might be the right answer. Often this works how the user wants and no significant changes are necessary. -o : Preserve user ownership (which is restricted to only superusers when dealing with other user’s files).
-list-only : Only show the list of files that rsync would transfer. -n : Dry run the command without transferring files. But, some of those might be contrary to what a user needs, so breaking it out into the specific functionality might be the right answer. Often this works how the user wants and no significant changes are necessary. -o : Preserve user ownership (which is restricted to only superusers when dealing with other user’s files).  -r : Recurse through directories (as opposed to only working on files in the current directory). The -a is equivalent to -rlptgoD, which breaks down to: Passing parameters such as -a for “archive” is quite common as it is a “meta-parameter” that automatically invokes a handful of others for you. It’s ordinarily desirable to pass rsync a few parameters to ensure things behave the way a human would expect them to. In its simplest form, rsync can be told to ensure that a file in one location should be the same in a second location in a filesystem. On the command line, rsync is generally invoked using a handful of parameters to define how it should behave since it’s a flexible tool. Linux system administration skills assessment. A guide to installing applications on Linux.
-r : Recurse through directories (as opposed to only working on files in the current directory). The -a is equivalent to -rlptgoD, which breaks down to: Passing parameters such as -a for “archive” is quite common as it is a “meta-parameter” that automatically invokes a handful of others for you. It’s ordinarily desirable to pass rsync a few parameters to ensure things behave the way a human would expect them to. In its simplest form, rsync can be told to ensure that a file in one location should be the same in a second location in a filesystem. On the command line, rsync is generally invoked using a handful of parameters to define how it should behave since it’s a flexible tool. Linux system administration skills assessment. A guide to installing applications on Linux. LINUX GRSYNC DOWNLOAD
Download RHEL 9 at no charge through the Red Hat Developer program. Working with rsync is easy and can be used on the command line, in scripts, and some tools wrap it in a nice UI for managing tasks. This is also the case with macOS, *BSDs, and other Unix-like operating systems. Since it comes packaged with most Linux distributions by default, it should be easy to get started. It can also do a quick hash check of files on the source and destination to determine whether or not it needs to transfer a new copy, possibly saving significant time and bandwidth. To accomplish this efficiently, by default, it will check the modification times of files. 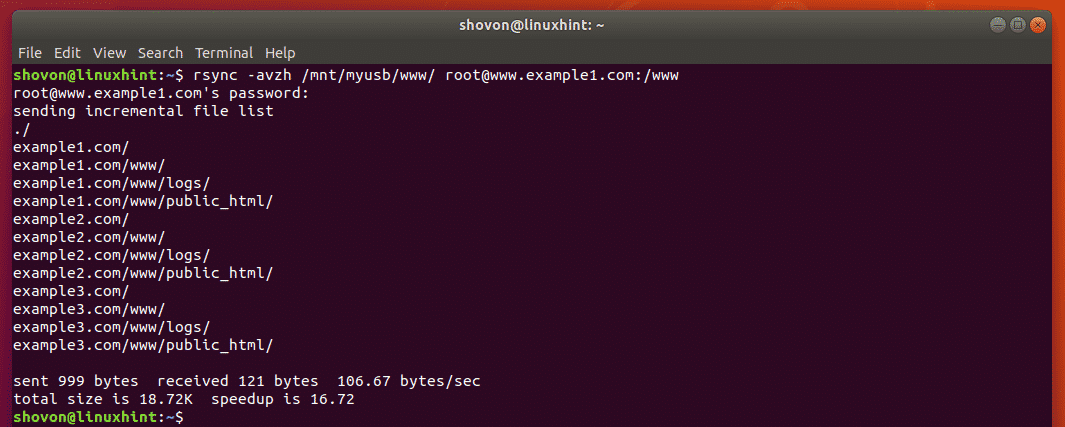
Also, rsync provides the ability to synchronize a directory structure (or even a single file) with another destination, local or remote. It checks to see if files exist in the destination before sending them, saving bandwidth and time for everything it skips. The rsync tool can recursively navigate a directory structure and update a second location with any new/changed/removed files. One of the most useful tools in a sysadmin’s belt for this kind of task is rsync. Admins (or normal users) often need to back up files or keep them in sync between multiple places (including local and remote) without transferring and overwrite all files on the target every time.








 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
